What is MABR?
The Membrane Aerated Biofilm Reactor (MABR) is an advanced biological treatment technology that utilizes a gas-permeable membrane to deliver oxygen directly to biofilms growing on the membrane surface. This method enhances treatment efficiency and reduces energy consumption compared to conventional aeration methods.
Key Features
- Low-energy oxygen delivery
- Simultaneous nitrification and denitrification (SND)
- Compact footprint
- Scalable and modular design
- Reduced sludge production
How MABR Works
In an MABR system, oxygen is supplied through the lumen of hollow-fiber or flat-sheet membranes. These membranes allow oxygen to diffuse into the biofilm, where aerobic and anoxic zones develop. The unique biofilm structure supports both nitrifying and denitrifying bacteria, enabling nitrogen removal without external carbon addition.
Process Flow Diagram of MABR
The following flow diagram illustrates a typical MABR treatment process, including influent pretreatment, biofilm reactor operation, and final effluent polishing steps.
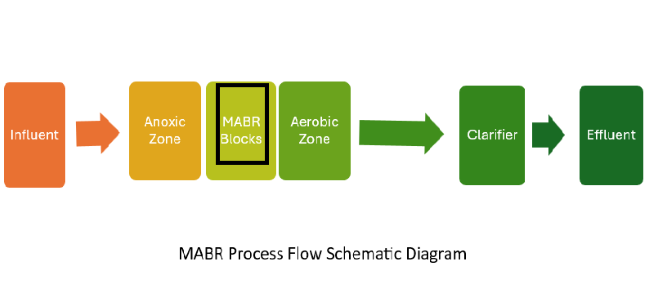
Applications
MABR systems are ideal for municipal and industrial wastewater treatment, especially in decentralized or small-footprint settings. They are also suitable for upgrading existing plants to meet stricter nutrient limits.
Advantages Over Conventional Systems
- Up to 90% energy savings in aeration
- Improved nitrogen removal
- Smaller reactor volumes
- Flexible installation options (submerged or sidestream)
